
Foods high in potassium are essential for heart, muscle, and nerve health—but choosing the right sources depends on portion size, preparation method, and individual health conditions.
Most people know potassium is “good for you,” yet few understand how much they actually consume or when too much becomes risky. That confusion leads to poor food choices, especially for people with blood pressure issues, kidney concerns, or restrictive diets. This guide breaks it down clearly—what to eat, how to compare foods, and when to be careful.
Foods high in potassium means foods that contain a large amount of the mineral potassium, an essential nutrient your body needs to function properly.
Potassium helps:
Regulate heart rhythm
Support muscle movement
Maintain nerve signals
Balance fluids and sodium levels
When a food is called “high in potassium,” it typically provides a significant portion of the daily recommended intake (around 2,600–3,400 mg for adults) in a normal serving size.
Examples of foods high in potassium include:
Spinach and other leafy greens
Bananas and avocados
Lentils and beans
Sweet potatoes
Yogurt and certain fish
In simple terms, foods high in potassium are nutrient-rich foods that help keep your heart, muscles, and nerves working smoothly, when eaten in the right amounts.
Potassium is an essential dietary mineral and electrolyte. It helps:
Most healthy people can safely meet this through food alone—not supplements.
| Food | Potassium (mg) | Density |
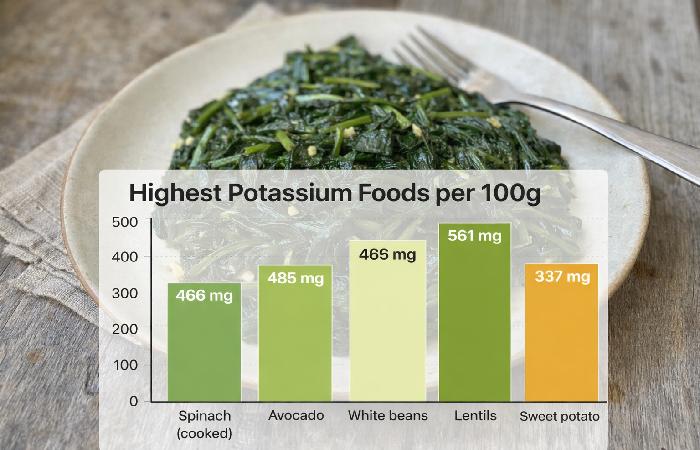
| Avocado | ~485 mg | Very High |
| Spinach (cooked) | ~466 mg | High |
| Sweet potato | ~337 mg | High |
| Banana | ~358 mg | Moderate |
| Yogurt | ~141 mg | Moderate |
If potassium levels are high, the goal is to choose lower-potassium alternatives while maintaining nutrition.
This approach is commonly recommended in renal and cardiac diets.
India’s traditional diet already includes many potassium-rich foods:
| Indian Food | Potassium Level |
| Dal (lentils) | High |
| Coconut water | High |
| Banana (Elaichi) | Moderate |
| Drumstick (moringa) | Very High |
| Spinach (palak) | High |
| Country | Common Sources | Notes |
| India | Lentils, bananas | Plant-based heavy |
| USA | Potatoes, dairy | High sodium risk |
| Japan | Seaweed, fish | Mineral-dense |
| Brazil | Beans, avocado | Natural intake |
| UK | Root vegetables | Seasonal variation |
Always follow medical advice if potassium restriction is recommended.
| Instead of | Choose |
| Banana | Apple |
| Potato | Rice |
| Spinach | Cabbage |
Foods high in potassium play a vital role in supporting heart health, muscle function, nerve signaling, and fluid balance. But the real takeaway isn’t simply to “eat more potassium”—it’s to choose the right sources, in the right amounts, for your body and health goals. While vegetables, legumes, fruits, and traditional foods offer excellent natural potassium, portion size, cooking methods, and individual health conditions make a big difference.
1. What food is highest in potassium?
Cooked spinach and legumes are among the highest natural sources per serving.
2. Are bananas the best source of potassium?
No. They are moderate compared to lentils, spinach, and avocados.
3. How much potassium is too much?
Above 5,000 mg daily may be risky for certain health conditions.
4. Can potassium lower blood pressure?
Yes, when balanced with low sodium intake.
5. Is coconut water high in potassium?
Yes, but portion size matters.
6. Should athletes eat more potassium?
Often yes, due to electrolyte loss from sweat.
7. Are supplements better than food?
No. Food sources are safer and better absorbed.
8. Can cooking reduce potassium?
Yes, boiling and pressure-cooking reduce levels.
9. Is potassium safe for kidney patients?
Only under medical supervision.
10. Which diet is naturally potassium-rich?
Plant-forward diets with legumes and vegetables.